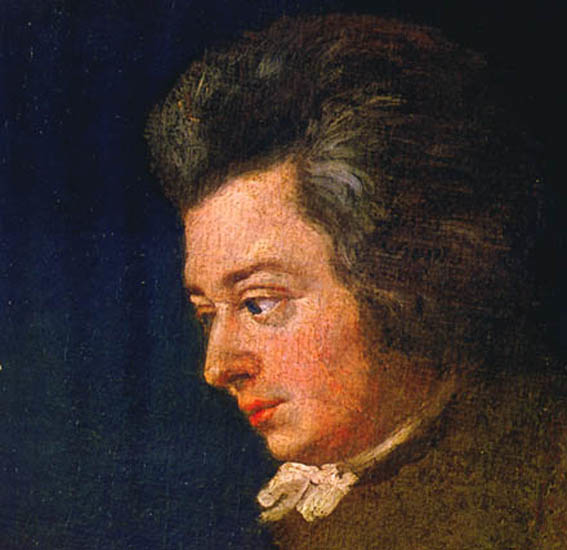The Well-Tempered Ear
FREE birthday bash for Johann Sebastian Bach is this Saturday in Madison
4 Comments
PLEASE HELP THE EAR. IF YOU LIKE A CERTAIN BLOG POST, SPREAD THE WORD. FORWARD A LINK TO IT OR, SHARE IT or TAG IT (not just “Like” it) ON FACEBOOK. Performers can use the extra exposure to draw potential audience members to an event. And you might even attract new readers and subscribers to the blog.
By Jacob Stockinger
The Ear thinks of this week’s Bach Around the Clock — which runs March 6-10 — as a double celebration.
The primary one is to mark the 339th birthday of composer Johann Sebastian Bach (below, March 20, 1685-July 28, 1750), whom many consider to be the Big Bang of Western classical music.
The second celebration is to honor the late Madison violist Marika Fischer Hoyt (below), who with help resurrected Bach Around the Clock in Madison after it had been dropped by Wisconsin Public Radio.
Talented, hard-working and congenial, Fischer — who died a year ago of cancer — was a fixture of the local music scene. She was a member of the Wisconsin Chamber Orchestra and spent 20 years playing in the Madison Symphony Orchestra. An outstanding chamber musician, she also helped found and played in the Ancora String Quartet.
An avid proponent of early music using period instruments and historically informed performance practices, Fischer Hoyt helped found and play in the weekly free Just Bach concerts. She performed regularly with the Madison Bach Musicians and with an early music string group she helped found, Sonata à Quattro.
Here is a link to a complete schedule on the BATC website:
The Ear thinks Marika would be very pleased and proud of this year’s event.
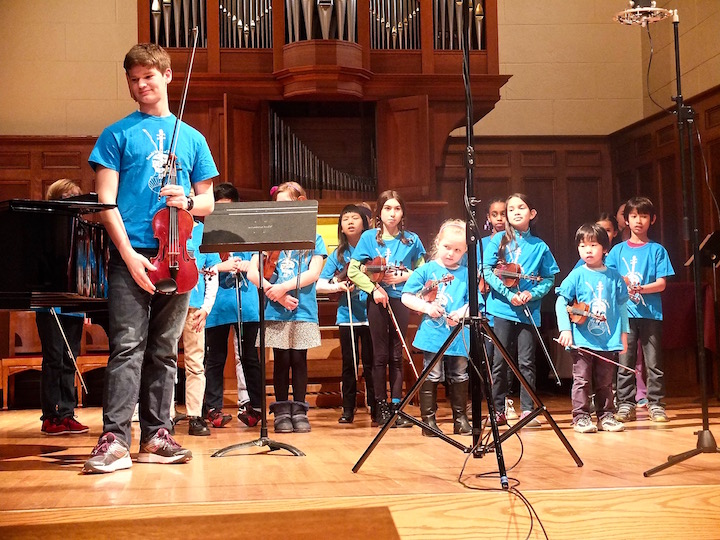
It will feature Bach’s original choral and instrumental music in many genres and transcriptions. Soloists and groups of varying sizes will take part. And Bach’s music — so central to the repertoire and all levels of musicianship — will be performed by students (below are members of the Suzuki Strings), by amateurs and by professionals (in the YouTube video at the bottom) — making BATC a truly community-wide celebration of Bach.
The hours for the Birthday Bash concert, which used to run 12 hours, have been cut back to a reasonable and accessible 10 a.m.-5 p.m. at St. Andrew’s Episcopal Church, 1833 Regent St., on Madison’s near west side. But a birthday cake will still be cut at the end.
And in case you want to duck in and out or catch certain performances or performers, here is a full program schedule for Saturday:
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1CIRby29h6wZjyngZgyMPpTrLNiMC_1OR/view
You can find links to all other events and programs — printed in blue — on the main website for the March 6-10 festival.
Performances by performers in their own homes and studios will air online as part of the Virtual Festival held of BATC’s YouTube channel, starting at midnight on this Sunday, March 10. Its runs without a time limit and can be accessed worldwide.
Here is a link to the YouTube channel, which also has past performances
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCHBRPHSGd_fNECp-qrWsqlQ
Have you attended or heard other Bach Around the Clocks?
What do you think of the celebration?
The Ear wants to hear.
Tags: #BlogPost, #BlogPosting, #FacebookPost, #FacebookPosting, #GoogleAlert, #Hard Work, #YouTubevideo, 2021, 2022, 2023, 2024, accessible, Ancora String Quartet, Android, Arts, attend, Bach Around the Clock, Baroque, BATC, birthday, blog, Brain, cake, cancer, Cantata, celebration, Cello, central, Chamber music, choral music, chorus, church, Classical music, clavichord, community, complete, composer, Concert, concerto, congenial, cut, dead, death, die, died, Early music, Episcopal, event, Facebook, festival, free, fugue, genre, Google, Google Alert, group, harpsichord, hear, historically informed performance practices, Home, honor, instrument, instrumental, Jacob Stockinger, Johann Sebastian Bach, Keyboard, link, Madison, Madison Bach Musicians, Madison Symphony Orchestra, Marika Fischer Hoyt, memory, Music, Musician, musicianship, online, Orchestra, organ, original, OS, Overture, Overture Center, partita, Passion, performance, performer, period instruments, Pianist, Piano, Prelude, program, Protestant, reasonable, repertoire, repertory, share, singer, Singing, soloist, Sonata, Sonata à Quattro, Spple, St. Andrew's Episcopal Church, String quartet, strings, studio, Suite, Suzuki, Suzuki Strings, symphony, tag, talent, The Ear, transcription, tumor, United States, University of Wisconsin-Madison School of Music, University of Wisconsin–Madison, Viola, Violin, violist, virtual, vocal music, volinist, Website, Wisconsin Chamber Orchestra, wisconsin public radio, worldwide, you, YouTube, ytalented
Making music saves senior brains, studies find
3 Comments
PLEASE HELP THE EAR. IF YOU LIKE A CERTAIN BLOG POST, SPREAD THE WORD. FORWARD A LINK TO IT OR, SHARE IT or TAG IT (not just “Like” it) ON FACEBOOK. Performers can use the extra exposure to draw potential audience members to an event. And you might even attract new readers and subscribers to the blog.
By Jacob Stockinger
If you are a senior and think that making music— even as a beginner — is for younger people, you couldn’t be more wrong.
A newly released British study offers convincing evidence that singing in a choir (below top, the now-defunct UW-Madison Choral Union) and playing an instrument (below bottom) helps to boost memory, and save the brains of older people, possibly averting or postponing cognitive decline, dementia and possibly Alzheimer’s disease.
Here are links, on Classic FM radio station’s website, to the stories about the two studies:
https://www.classicfm.com/discover-music/piano-choir-keeps-brain-memory-active/
https://www.classicfm.com/music-news/piano-lessons-older-age-delay-dementia/
How does your own experience measure up to findings in the studies?
The Ear wants to hear.
Tags: #BlogPost, #BlogPosting, #FacebookPost, #FacebookPosting, Arts, audience, Bach, beginner, beginning, blog, boost, Brain, brass, British, Cello, Chamber music, Choir, choral music, church, Classic FM, Classical music, cognition, cognitive, cognitive decline, composer, Concert, concerto, dementia, Early music, Education, elderly, England, English, Exeter University, Facebook, Great Britain, instrument, Jacob Stockinger, Johann Sebastian Bach, link, Ludwig van Beethoven, Madison, Madison Symphony Orchestra, memory, Mozart, Music, Music education, music lessons, Musician, old, opera, Orchestra, Piano, play, playing, senior citizen, seniors, share, sing, singer, Singing, Sonata, Student, symphony, tag, The Ear, UK, United States, university, University of Wisconsin-Madison School of Music, University of Wisconsin–Madison, Violin, vocal music, Website, Wisconsin, Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, woodwind, young, younger
Why do we like sad music?
6 Comments
PLEASE HELP THE EAR. IF YOU LIKE A CERTAIN BLOG POST, SPREAD THE WORD. FORWARD A LINK TO IT OR, SHARE IT or TAG IT (not just “Like” it) ON FACEBOOK. Performers can use the extra exposure to draw potential audience members to an event. And you might even attract new readers and subscribers to the blog.
By Jacob Stockinger
Why does sad music — or sad art — appeal to so many of us?
One psychologist and brain researcher — Matthew Sachs of Columbia University (below) — says it serves an evolutionary and social purpose by eliciting empathy for other humans and purging us of negative emotions, according to a story and interview on NPR (National Public Radio).
To The Ear, the explanation sounds a lot like the ancient Greek philosophy of catharsis that was the cornerstone justification for the public staging of great ancient tragedies by writers such as Aeschylus, Sophocles and Euripides, and of course the famous tragedies of Shakespeare such as “Romeo and Juliet,” Hamlet” and “King Lear” that were famously popular dramas as well as great masterpieces of Western literature.
Consider the case of Samuel Barber’s often-played “Adagio for Strings,” analyzed at length in a book called “The Saddest Music in the World.” Or perhaps the “Pathétique” piano sonata by Beethoven and the “Funeral March” piano sonata by Chopin. Or the requiems by Mozart and Brahms.
Or consider the music “Beautiful Sadness” by the contemporary composer Cliff Masterson (below). You can hear it in the YouTube video at the bottom.
Here is a link to the NPR story that discusses “the rules of musical melancholy.”
You can read it, or take four minutes to listen to it:
https://www.npr.org/2023/09/06/1173993223/understanding-the-joy-that-many-find-in-sadness
Do you find solace in sad music?
Does sad music make you feel better?
Do you have a favorite piece of sad music?
Or maybe a favorite tragic play, opera or work of art?
The Ear wants to hear.
Tags: #BlogPost, #BlogPosting, #FacebookPost, #FacebookPosting, #YouTubevideo, Adagio for Strings, Aeschylus, Ancient Greece, appeal, arranger, Art, Arts, audience, Bach, Baroque, beautiful, Beethoven, blog, Brahms, Brain, Britten, catharsis, Cello, Chamber music, Chopin, choral music, Classical music, Cliff Masterson, Columbia University, composer, Concert, concerto, conductor, contemporary, cornerstone, discuss, Early music, emotion, empathy, Euripides, evolution, evolutionary, explanation, Facebook, favorite, feel, funeral march, great, Greek tragedy, Hamlet, happiness, happy', Hollywood, human, interview, Jacob Stockinger, Johann Sebastian Bach, journalism, Joy, justification, King Lear, link, literature, Ludwig van Beethoven, Madison, Madison Symphony Orchestra, Matthew Sachs, melancholy, movie, Mozart, Music, National Public Radio, negative, news, NPR, opera, Orchestra, Overture Center, pathetique, philosophy, Piano, play, pleasure, popular, psychologist, psychology, purge, purpose, Radio, Requiem, research, rid, Romeo and Juliet, rule, sad, sadness, science, scientist, score, Shakespeare, share, social, solace, Sonata, Sophocles, soundtrack, story, symphony, tag, The Ear, tragedy, Tragic, United States, University of Wisconsin-Madison School of Music, University of Wisconsin–Madison, Viola, Violin, vocal music, Western, Wisconsin, Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, work of art, Writer, YouTube
Music builds brain health. Which composers and pieces would you recommend?
6 Comments
PLEASE HELP THE EAR. IF YOU LIKE A CERTAIN BLOG POST, SPREAD THE WORD. FORWARD A LINK TO IT OR, SHARE IT or TAG IT (not just “Like” it) ON FACEBOOK. Performers can use the extra exposure to draw potential audience members to an event. And you might even attract new readers and subscribers to the blog.
By Jacob Stockinger
If you think music education and music lessons are only for young people who are still growing and maturing, you couldn’t be more wrong.
More and more research studies show that in adults and older people, even in Alzheimer’s patients, music has force and can break through.
Music is — like many other kinds of art including poetry, dance and paintings — a key that unlocks the plasticity of the human brain (below is an image from Shutterstock) and the brain’s ability to grow and endure in a healthy manner.
Here is one of the most recent studies that was covered in a story by NPR (National Public Radio), which you can read or listen to:
https://www.npr.org/sections/health-shots/2023/04/03/1167494088/your-brain-on-art-music-dance-poetry
The Ear finds it convincing food for thought.
Certain genres of music, for example, come to mind as brain-healthy. Think Schubert. Art songs which combine music and words, even poetry, seem an especially likely candidate.
String quartets and theme-and-variations also come to mind as artistic and brain-developing genres. So does the sonata form that is used to develop and establish harmonic and thematic logic in symphonies and concertos as well as sonatas.
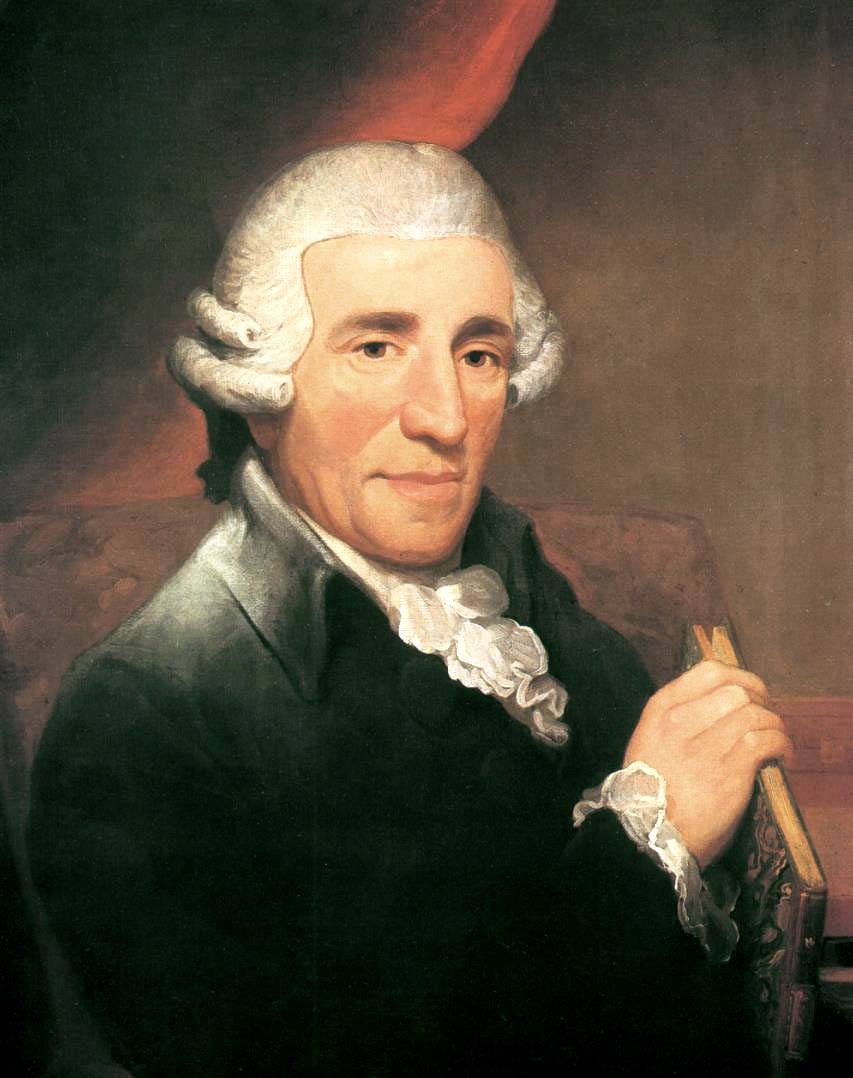
As for specific composers, The Ear thinks Johann Sebastian Bach (below) stands out as a one whose music requires active listening and critical thinking.
Preludes and fugues by Johann Sebastian Bach (below and in the YouTube video at the bottom where Friedrich Gulda plays the Prelude and Fugue No. 1 of the WTC) in The Well-Tempered Clavier and his many suites and Beethoven’s string quartets, especially the late ones, are individual challenging works that do the same.
Are there musical genres that you think are good for the brain and would recommend?
Are there certain composers you think are especially helpful in building brain health?
Are there any particular pieces that you think also work toward brain health and plasticity?
The Ear wants to hear.
Tags: #BlogPost, #BlogPosting, #FacebookPost, #FacebookPosting, #YouTubevideo, adults, Alzheimer's, Art, art songs, Arts, audience, Bach, Baroque, Beethoven, blog, Brain, build, candidate, challenge, challenging, Chamber music, children, choral music, Classical music, composer, concerto, connectivity, creativity, critical thinking, dance, develop, Disease, Early music, Education, endure, Facebook, force, Franz Schubert, Friedrich Gulda, fugue, genetics, genre, grow, Gulda, harmonic, harmony, Health, human brain, Jacob Stockinger, Johann Sebastian Bach, link, listen, listening, logic, Ludwig van Beethoven, mature, medicine, Music, music lessons, National Public Radio, NPR, old people, Orchestra, painting, Piano, piece, plasticity, poem, Poetry, Prelude, read, recommend, research, Schubert, science, seniors, share, Sonata, song, String quartet, structure, study, Suite, symphony, synapse, tag, technology, The Ear, thematic, theme, theme and variations, think, Violin, vocal music, Well-Tempered Clavier, wisconsin public radio, Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, words, work, WPR, young people, YouTube
One piano lesson made all the difference
1 Comment
PLEASE HELP THE EAR. IF YOU LIKE A CERTAIN BLOG POST, SPREAD THE WORD. FORWARD A LINK TO IT OR, SHARE IT or TAG IT (not just “Like” it) ON FACEBOOK. Performers can use the extra exposure to draw potential audience members to an event. And you might even attract new readers and subscribers to the blog.
By Jacob Stockinger
Not long ago, NPR and Wisconsin Public Radio featured a moving story from the website “Hidden Brain” and its series of profile called “My Unsung Hero.”
It told the simple story of a single piano lesson — and how just one short sentence at this piano lesson proved both ordinary and momentous – and made all the difference, changing the course of a young boy’s life.
The Ear found it inspiring. And it provoked some of his own memories of important music lessons and music teachers as well as other subjects and other influential teachers in school.
He hopes you will also like it and share it, perhaps with a friend who had a similar experience or with a special teacher who influenced you and made an important difference in your life.
Here is a link:
Did you ever have a similar experience with a music teacher and music lesson?
Or find an “unsung hero” in music or another field of education who made a big difference?
Please tell us about it.
The Ear wants to hear.
Tags: #BlogPost, #BlogPosting, #FacebookPost, #FacebookPosting, Arts, big, blog, boy, Brain, Classical music, difference, Education, Facebook, hear, hero, Hidden Brain, influence, Jacob Stockinger, lesson, life, Madison, Music, Music lesson, My Unsung Hero, National Public Radio, NPR, ordinary, Piano, piano lesson, piano teacher, sentence, share, short, simple, single, special, story, tag, Teacher, tell, The Ear, The Well-Tempered Ear, Website, wisconsin public radio, WPR
Classical music: What happens when Shakespeare and Benjamin Britten meet Andy Warhol and The Factory? The University Opera explores a new spin on an old tale
Leave a Comment
PLEASE HELP THE EAR. IF YOU LIKE A CERTAIN BLOG POST, SPREAD THE WORD. FORWARD A LINK TO IT OR, SHARE IT or TAG IT (not just “Like” it) ON FACEBOOK. Performers can use the extra exposure to draw potential audience members to an event. And you might even attract new readers and subscribers to the blog.
ALERT: At 7:30 p.m. this Thursday night, Nov. 14 — the night before it opens the opera production below — the UW-Madison Symphony Orchestra, under conductor Oriol Sans, will perform a FREE concert in the Mead Witter Foundation Concert Hall of the new Hamel Music Center, 740 University Avenue, next to the Chazen Museum of Art. The program offers Darius Milhaud’s “The Creation of the World,” Maurice Ravel’s “Mother Goose Suite” and Franz Joseph Haydn’s Symphony No. 101 “The Clock.”
By Jacob Stockinger
The Big Event in classical music this week in Madison is the production by the University Opera of Benjamin Britten’s “A Midsummer Night’s Dream.”
It is a chance to see what happens when Shakespeare (below top) meets Britten (below bottom) through the lens of the Pop art icon Andy Warhol.
The three-hour production – with student singers and the UW-Madison Symphony Orchestra under conductor Oriol Sans — will have three performances in Music Hall, at the foot of Bascom Hill: this Friday night, Nov. 15, at 7:30; Sunday afternoon, Nov. 17, at 2 p.m.; and Tuesday night, Nov. 19, at 7:30 p.m.
Tickets are $25 for the general public; $20 for seniors; and $10 for students.
For more information about the production and how to obtain tickets, go to: https://www.music.wisc.edu/event/university-opera-a-midsummer-nights-dream/2019-11-15/
For more information about the performers, the alternating student cast and a pre-performance panel discussion on Sunday, go to: https://www.music.wisc.edu/wp-content/uploads/2019/10/A-Midsummer-Nights-Dream-Media-release.pdf
And here are notes by director David Ronis (below, in a photo by Luke Delalio) about the concept behind this novel production:
“When the artistic team for A Midsummer Night’s Dream met last spring, none of us expected that we would set Britten’s opera at The Factory, Andy Warhol’s workspace-cum-playspace.
“For my part, I wanted to find a way to tell this wonderful story that would be novel, engaging, entertaining, and thought-provoking.
“I only had one wish: that we did a production that did not feature fairies sporting wings – a representation that, to me, just seemed old-fashioned and, frankly, tired.
“As we worked on the concept, we found that The Factory setting allowed us to see the show in a new, compelling light and truly evoked its spirit and themes. The elements of this “translation” easily and happily fell into place and now, six months later, here we are!
“A Midsummer Night’s Dream tells the intersecting stories of three groups of characters – Fairies, Lovers and Rustics – and its traditional locale is that of a forest, the domain of Oberon, the Fairy King. (You can hear the Act 1 “Welcome, Wanderer” duet with Puck and Oberon, played by countertenor David Daniels, in the YouTube video at the bottom.)
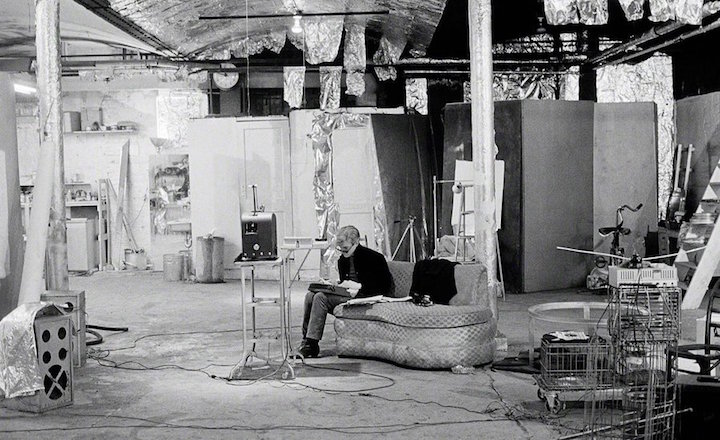
“In our production, the proverbial forest becomes The Factory, where our Oberon, inspired by Andy Warhol (below, in a photo from the Andy Warhol Museum), rules the roost. He oversees his world – his art, his business, and “his people.” He is part participant in his own story, as he plots to get even with Tytania, his queen and with whom he is at odds; and part voyeur-meddler, as he attempts to engineer the realignment of affections among the Lovers.
“Tytania, in our production, is loosely modeled on Warhol’s muse, Edie Sedgwick (below top), and Puck resembles Ondine (below bottom), one of the Warhol Superstars.
The Fairies become young women in the fashion or entertainment industries, regulars at The Factory; the Lovers, people who are employed there; and the Rustics, or “Rude Mechanicals,” blue-collar workers by day, who come together after hours to form an avant-garde theater troupe seeking their 15 minutes of fame.
“For all these people, The Factory (below, in a photo by Nat Finkelstein) is the center of the universe. They all gravitate there and finally assemble for the wedding of Theseus and Hippolyta – in this setting, a rich art collector and his trophy girlfriend.
“Magic is an important element in Midsummer. In the realm of the fairies, Oberon makes frequent use of magical herbs and potions to achieve his objectives. In the celebrity art world of mid-1960s New York City, those translate into recreational drugs.
“The people who work in and gather at The Factory are also are involved in what could be called a type of magic – making art and surrounding themselves in it. They take photographs, create silk screen images, hang and arrange Pop art, and party at The Factory.
“Not only does this world of creative magic provide us with a beautiful way to tell the story of Midsummer, but it also becomes a metaphor for the “theatrical magic” created by Shakespeare and Britten, and integral to every production.
“We hope you enjoy taking this journey with us, seeing A Midsummer Night’s Dream in perhaps a new way that will entertain and delight your senses and, perhaps, challenge your brain a bit.”
Tags: #AMIdsummerNight'sDream, #AndyWarhol, #AndyWarholMuseum, #BascomHill, #BenjaminBritten, #BlogPost, #ChazenMuseumofArt, #ChoralMusic, #CountertenorSinger, #DariusMilhaud, #DavidDaniels, #DavidRonis, #EdieSedgwick, #FacebookPost, #FacebookPosting, #FranzJosephHaydn, #Fridaynight, #HamelMusicCenter, #MadisonWisconsin, #MauriceRavel, #MeadWitterFoundationConcertHall, #MeadWitterSchoolofMusic, #Mezzo-sopranoSinger, #MotherGoose, #MusicHall, #NewYorkCity, #Old-fashioned, #OperaAria, #OperaCast, #OperaMusic, #OrchestralAccompaniment, #OrchestralMusic, #OriolSans, #PanelDiscussion, #PopArt, #SaturdayNight, #SeniorCitizen, #SilkScreen, #SopranoSinger, #Sundayafternoon, #TenorSinger, #TheCreation, #TheCreationoftheWorld, #TheEar, #TheFactory, #UniversityofWisconsin-Madison, #UniversityOpera, #UW-MadisonSymphonyOrchestra, #VocalMusic, #WilliamShakespeare, #YouTubevideo, A Midsummer Night's Dream, act, affections, afternoon, alternating, Andy Warhol, Andy Warhol Museum, aria, Art, artistic, Arts, assemble, audience, avant-garde, Bascom Hill, beautiful, Benjamin Britten, big, blog, blue-collar, Brain, Britten, Business, cast, celebrity, center, challenge, character, Chazen Museum of Art, choral music, Classical music, Clock, collector, compelling, composer, concept, Concert, conductor, countertenor, Creation, Creation of the World, creative, Darius Milhaud, David Daniels, David Ronis, delight, director, discussion, domain, drug, duet, Edie Sedgwick, element, employed, engaging, engineer, enjoy, entertaining, Entertainment, event, evoke, expect, expectations, Facebook, factory, fairies, fairy, fame, fashion, forest, Franz Joseph Haydn, free, Friday, girlfriend, gravitate, Hamel Music Center, Haydn, help, herbs, his, hours, icon, image, industries, industry, integral, Jacob Stockinger, journey, King, lens, light, like, link, locale, lover, Madison, magic, magical, Maurice Ravel, Mead Witter Foundation Concert Hall, Mead Witter School of Music, mechanical, meddler, meet, metaphor, Mezzo-soprano, Milhaud, minutes, modeled, month, Mother Goose, muse, Museum, Music, Music Hall, new, New York City, night, notes, novel, Oberon, objective, odds, Ondine, open, opera, Orchestra, orchestral, Oriol Sans, panel discussion, party, People, performer, photographs, plots, Pop art, post, posting, potion, production, public, Puck, queen, Ravel, realign, realignment, realm, recreational, regular, representation, rich, role, rude, rustic, Saturday, senior, senses, setting, Shakespeare, share, show, silk screen, singer, soprano, space, spin, spirit, Sport, Spring, story, Student, Suite, Sunday, superstar, symphony, tag, tale, team, tell, tenor, The Ear, The Factory, theater, theme, thought provoking, tickets, tired, traditional, translation, trophy, troupe, Tytania, United States, universe, University of Wisconsin-Madison School of Music, University of Wisconsin–Madison, University Opera, UW-Madison Symphony Orchestra, video, vocal music, voyeur, way, wedding, week, welcome, wings, Wisconsin, women, work, workspace, world, YouTube
Classical music: The UW-Madison’s Pro Arte Quartet delivers a perfect program of superb music by Haydn, Mozart and Schubert
Leave a Comment
By Jacob Stockinger
Here is a special posting, a review written by frequent guest critic and writer for this blog, John W. Barker. Barker (below) is an emeritus professor of Medieval history at the University of Wisconsin-Madison. He also is a well-known classical music critic who writes for Isthmus and the American Record Guide, and who hosts an early music show once a month on Sunday morning on WORT-FM 89.9 FM. For years, he served on the Board of Advisors for the Madison Early Music Festival and frequently gives pre-concert lectures in Madison.
By John W. Barker
While snow may have restricted the audience attending the Pro Arte Quartet (below, in a photo by Rick Langer) on Saturday night, those who came were amply rewarded with a virtually perfect program of superb music.
The program brought together three Austrian works, two by those Classical-era titans, Franz Joseph Haydn and Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, and the third by the Austrian early Romantic Franz Schubert.
The combination of the first two was particularly stimulating, an opportunity to reckon how different from each other were these composers who are so often bracketed together.
The E-flat Quartet is No. 3 in the Op. 50 set that some commentators have viewed as the response by Haydn (below) to the set of six quartets that Mozart had recently published in Haydn’s honor.
Deliberately, Haydn chose to avoid matching Mozart’s lyricism and rich imagination, turning instead to statements of strength in austere textures.
Composed in 1790, a year before his death and only three years after the Haydn work, the Quartet in B-flat, K. 589, by Mozart (below) was his penultimate quartet, part of a series to be written for the King of Prussia who played the cello, which is featured prominently in the quartet.
Here we have a Mozartian style that is expansive and exploratory. Amid music of great lyric beauty and even vivacity, we have a Menuetto third movement whose Trio, or midsection, is remarkably dark and ambiguous. (You can hear a period-instrument performance of the third movement in the YouTube video at the bottom)
The Pro Arte players brought out the individuality of the two different styles quite beautifully. To my ears, the viola lines were delivered with notable strength and color by Sally Chisholm.
The final work, and the longest, was one of Schubert’s amazing late quartets. The No. 13 in A minor, D. 804), from 1824 is known as the “Rosamunde” Quartet because the second movement is the elaboration by Schubert (below) of the lovely melody in the well-known interlude in his incidental music for the play of that title.
Despite a somewhat moody first movement, the work as a whole is suffused with Schubert’s very special, very personal lyricism. Analyses of it can be instructive, but ultimately this remains music for the soul, not just the brain, I think.
The Pro Arte understands that well, and gave a generous demonstration of its beauties.
It proved such a wonderful concert, for which we can only give warm thanks to the UW-Madison’s Mead-Witter School of Music where the Pro Arte Quartet has been an artist-in-residence since World War II.
Tags: #ChamberMusic, #FranzJosephHaydn, #FranzSchubert, #MadisonEarlyMusicFestival, #MeadWitterSchoolofMusic, #ProArteQuartet, #SecondWorldWar, #StringQuartet, #UniversityofWisconsin-Madison, #WorldWarII, amazing, ambiguous, American Record Guide, analyses, analysis, artist, artist-in-residence, Arts, austere, Austria, Austrian, beauty, bracket, Brain, Cello, Chamber music, Classical, Classical music, color, composer, Concert, critic, dark, death, demonstration, drama, elaboration, emeritus, expansive, exploratory, fina, Franz Schubert, generous, Haydn, historically informed performance practices, History, honor, imagination, incidental, incidental music, individuality, instrument, interlude, Isthmus, Jacob Stockinger, John W. Barker, King, late, lecture, line, long, longest, lovely, lyrical, lyricism, Madison, Medieval, melody, minuet, moody, morning, Mozart, Music, opportunity, perfect, period, period-instrument, personal, play, Pro Arte Quartet, professor, program, Prussia, residence, response, reward, Romantic, Rosamunde, Saturday night, section, set, snow, soul, statment, strength, String quartet, style, Sunday, texture, thanks, Titan, trio, United States, University of Wisconsin-Madison School of Music, University of Wisconsin–Madison, Viola, Violin, vivacity, warm, Wisconsin, Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, World War II, WORT-FM 89.9, YouTube
Classical music: Here are many of the major figures that classical music lost in 2017
2 Comments
By Jacob Stockinger
One of the traditional ways to start a new year is to take stock of the past year.
That often means compiling lists of the best performances, the best recordings, the best books, and so forth.
It also means listing the major figures who died in the past year.
Two of the more prominent classical music performers who died in 2017 were the renowned Russian baritone Dmitri Hvorostovsky (below top), who died of a brain tumor at 55, and the conductor Georges Prêtre (below bottom in a photo by Dieter Hagli for Getty Images).
There were many more, but they seem harder to find or to remember.
It seems to The Ear that such lists used to be more common.
It also seems to The Ear that many more of such lists for classical music are being incorporated into a overall lists of entertainers and celebrities in pop, rock, country, jazz, folk and even film stars who died. That is what National Public Radio (NPR) and The New York Times did this year.
Does that trend suggest that classical music is gradually and increasingly being marginalized or ignored? It is a reasonable question with, The Ear fears, a sad answer.
Does anyone else see it the same way?
But at least one reliable source – famed radio station WQXR-FM in New York City – has provided a list of performers, presenters and scholars of classical music who died in 2017.
Moreover, the list comes with generous sound and video samples that often make the loss more poignant.
Here is the link:
https://www.wqxr.org/story/music-made-classical-artists-lost-2017
Has someone been overlooked, especially among local figures?
If so, please use the COMMENT section to leave a name or even your reaction to the other deaths.
The Ear wants to hear.
Tags: answer, Arts, Arts and Entertainment, Bach, baritone, Baroque, Book, Brain, cancer, celebrities, celebrity, Cello, Chamber music, choral music, Classical music, Compact Disc, composer, concerto, country, death, Dmitri Hvorostovsky, Early music, entertainer, Entertainment, fear, figure, film, folk, Georges Prêtre, ignore, Jacob Stockinger, Jazz, list, Ludwig van Beethoven, marginalize, movie, Mozart, Music, National Public Radio, New Year, New York City, New York Times, NPR, opera, Orchestra, past, performance, performer, Piano, pop, question, Radio, recording, renown, Rock, star, symphony, The New York Times, trend, tumor, United States, University of Wisconsin-Madison School of Music, University of Wisconsin–Madison, Viola, Violin, vocal music, Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, WQXR-FM
Classical music: Live radio broadcasts from the Metropolitan Opera start their 87th season with the Verdi Requiem at NOON this Saturday on Wisconsin Public Radio.
Leave a Comment
By Jacob Stockinger
What is the longest-running classical music broadcast on American radio?
If you said the live Saturday matinee broadcasts from the Metropolitan Opera (below) in New York City, you got it right.
So, does that qualify the Met, and opera in general, as pop culture?
Does it do anything to reassure those who worry about the future of opera and classical music?
Anyway, the 87th broadcast season starts again on Wisconsin Public Radio this Saturday morning and runs through May 5.
Of course, not there are also the popular and more cinematic broadcasts of “Live From the Met in HD.” But many listeners still prefer the radio — which is FREE — to help them focus on the music, not the visual and theatrical aspects, and to use their imagination more.
On Saturday at the usual time of NOON — not 11:05 a.m. as was mistakenly first published here — the Met features a performance of the dramatic Requiem by opera great Giuseppe Verdi (below). (You can hear the operatic Dies Irae, or Day of Wrath, section in the YouTube video at the bottom.)
The Requiem will be conducted by James Levine (below), the now retired longtime artistic director of the Met.
The 90-minute performance will dedicated to the famed Russian baritone Dmitri Hvorostovsky (below bottom), who died two weeks ago from a brain tumor at age 55. For more information about the late singer, go to:
For as complete schedule of the works to be performed, which include well-known standards by Mozart, Rossini, Donizetti, Bellini, Verdi, Puccini, Wagner and Richard Strauss as well as a contemporary work by Thomas Adès, go to the WPR website:
https://www.wpr.org/metropolitan-opera-begins-its-87th-broadcast-season
Tags: Adès, Arts, Bellini, Brain, brain tumor, Broadcast, cancer, choral music, cinema, Classical music, composer, day, dedicated, Dmitri Hvorostovsky, Donizetti, drama, dramatic, future, Gaetano Donizetti, Giuseppe Verdi, imagination, Italy, Jacob Stockinger, James Levine, listener, Live From The Met in HD, matinee, Metropolitan Opera, Mozart, Music, New York City, opera, Orchestra, performance, pop, pop culture, Puccini, Radio, Requiem, Rossini, Saturday, schedule, Season, standard, Strauss, theater, theatre, theatrical, tumor, United States, visual, Wagner, Website, Wisconsin, wisconsin public radio, work, WPR, wrath, YouTube
Classical music: Charismatic Russian baritone Dmitri Hvorostovsky is dead at 55
4 Comments
By Jacob Stockinger
The charismatic Russian baritone Dmitri Hvorostovsky (below, in a 2006 photo by Richard Termine of The New York Times) had it all.
Most importantly, the great opera singer, concert singer and recitalist possessed a superb voice with wonderful tone and breath control that allowed him to even beat out Bryn Terfel to win Singer of the World at a competition in Cardiff, Wales.
But he also had handsome face and fit beefcake body that made him a believable actor in so many roles and proved a pleasure to watch on stage.
And what about that fabulous mane of prematurely white hair that became his signature?
But on Wednesday, the acclaimed Siberian singer Dmitri Hvorostovsky — who was well on his way to becoming a superstar — lost a two-year bout with brain cancer.
He died at 55 – but not after winning plaudits for unexpected appearances at the Metropolitan Opera (below) and Carnegie Hall even while he was ill.
Here are two obituaries.
The first comes from the Deceptive Cadence blog of National Public Radio (NPR) and features three samples of his singing as well as some memorable interview quotes, including the renowned singer’s unapologetic take on his own sex appeal (below) that landed him in People magazine:
And here is a longer obituary, also with samples, from The New York Times. It includes a lot of background about the singer’s early life and career:
https://www.nytimes.com/2017/11/22/arts/music/dmitri-hvorostovsky-dead.html
Did you ever see or hear Dmitri Hvorostovsky in person or perhaps in “Live From the Met in HD” broadcasts? (He sings two folk songs in the YouTube memorial video at the bottom.)
And for those of you can judge singers better than The Ear can, what was your opinion of the Russian baritone?
Did you have a favorite role or aria you liked him in?
The Ear wants to know.
Tags: Actor, appeal, aria, Arts, background, baritone, beefcake, believable, body, bout, Brain, breath, Broadcast, Bryn Terfeld, cancer, Cardiff, career, Carnegie Hall, charisma, choral music, Classical music, Competition, Concert, control, death, Dmitri Hvorostovsky, early, face, folk, folk song, hair, handsome, interview, Jacob Stockinger, life, Live From The Met in HD, Madison, magazine, mane, memorial, Metropolitan Opera, New York City, NPR, obituary, opera, People, plaudits, pleasure, praise, premature, quote, recital, role, Russia, Russian, sample, sex, sexy, Siberia, signature, singer, Singer of the World, superstar, tone, unexpected, United States, University of Wisconsin-Madison School of Music, University of Wisconsin–Madison, video, voice, Wales, white, win, YouTube
- May 2024
- April 2024
- March 2024
- February 2024
- January 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- September 2023
- August 2023
- July 2023
- June 2023
- May 2023
- April 2023
- March 2023
- February 2023
- January 2023
- December 2022
- October 2022
- September 2022
- June 2022
- May 2022
- April 2022
- March 2022
- July 2021
- June 2021
- May 2021
- April 2021
- March 2021
- February 2021
- January 2021
- December 2020
- November 2020
- October 2020
- September 2020
- August 2020
- July 2020
- June 2020
- May 2020
- April 2020
- March 2020
- February 2020
- January 2020
- December 2019
- November 2019
- October 2019
- September 2019
- August 2019
- July 2019
- June 2019
- May 2019
- April 2019
- March 2019
- February 2019
- January 2019
- December 2018
- November 2018
- October 2018
- September 2018
- August 2018
- July 2018
- June 2018
- May 2018
- April 2018
- March 2018
- February 2018
- January 2018
- December 2017
- November 2017
- October 2017
- September 2017
- August 2017
- July 2017
- June 2017
- May 2017
- April 2017
- March 2017
- February 2017
- January 2017
- December 2016
- November 2016
- October 2016
- September 2016
- August 2016
- July 2016
- June 2016
- May 2016
- April 2016
- March 2016
- February 2016
- January 2016
- December 2015
- November 2015
- October 2015
- September 2015
- August 2015
- July 2015
- June 2015
- May 2015
- April 2015
- March 2015
- February 2015
- January 2015
- December 2014
- November 2014
- October 2014
- September 2014
- August 2014
- July 2014
- June 2014
- May 2014
- April 2014
- March 2014
- February 2014
- January 2014
- December 2013
- November 2013
- October 2013
- September 2013
- August 2013
- July 2013
- June 2013
- May 2013
- April 2013
- March 2013
- February 2013
- January 2013
- December 2012
- November 2012
- October 2012
- September 2012
- August 2012
- July 2012
- June 2012
- May 2012
- April 2012
- March 2012
- February 2012
- January 2012
- December 2011
- November 2011
- October 2011
- September 2011
- August 2011
- July 2011
- June 2011
- May 2011
- April 2011
- March 2011
- February 2011
- January 2011
- December 2010
- November 2010
- October 2010
- September 2010
- August 2010
- July 2010
- June 2010
- May 2010
- April 2010
- March 2010
- February 2010
- January 2010
- December 2009
- November 2009
- October 2009
- September 2009
- August 2009
Archives
- 2,491,634 hits
Blog Stats
Recent Comments
| Brian Jefferies on Classical music: A major reass… | |
| welltemperedear on What made Beethoven sick and… | |
| rlhess5d5b7e5dff on What made Beethoven sick and… | |
| welltemperedear on Beethoven’s Ninth turns 200… | |
| Robert Graebner on Beethoven’s Ninth turns 200… |
Tags
#BlogPost #BlogPosting #ChamberMusic #FacebookPost #FacebookPosting #MeadWitterSchoolofMusic #TheEar #UniversityofWisconsin-Madison #YouTubevideo Arts audience Bach Baroque Beethoven blog Cello Chamber music choral music Classical music Compact Disc composer Concert concerto conductor Early music Facebook forward Franz Schubert George Frideric Handel Jacob Stockinger Johannes Brahms Johann Sebastian Bach John DeMain like link Ludwig van Beethoven Madison Madison Opera Madison Symphony Orchestra Mead Witter School of Music Mozart Music New Music New York City NPR opera Orchestra Overture Center performer Pianist Piano post posting program share singer Sonata song soprano String quartet Student symphony tag The Ear United States University of Wisconsin-Madison School of Music University of Wisconsin–Madison Viola Violin vocal music Wisconsin Wisconsin Chamber Orchestra wisconsin public radio Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart YouTube